MOKE
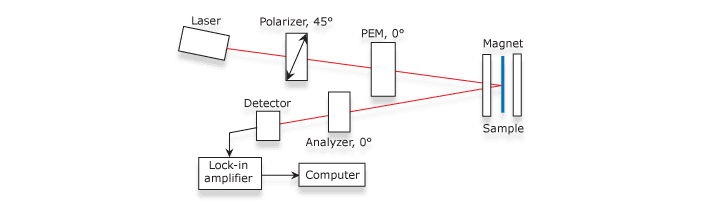
Magneto Optic Kerr Effect (MOKE) experiments are designed to detect small changes in polarization that occur because magnetic fields influence the polarization state of optical radiation as it passes through a transparent medium.
PEM Setting: quarter-wave retardation (λ/4)
Polarization Modulation: right and left circular polarized light
Lock-in reference: PEM’s 1st Harmonic
The modulated light is reflected by the sample, which is situated in the center of the electromagnet poles. Setting the analyzer angle to 0° greatly simplifies the mathematical relationship between the intensity ratios measured and the magneto-optical parameters. The following equation represents the resulting signal intensity. From the lock-in values the MOKE parameters θk and εk may be calculated.
![]()
Where:
V1f and V2f are the voltages of the first harmonic signals from the lock-in
VDC is the DC signal
J1 and J2 are Bessel function coefficients
The derivation of these equations may be found in the Magneto-Optic Kerr Effect Application Note.
APPLICATIONS
- Data Storage
- Disk Recording Systems
- Dynamic Studies of Film Growth
PEMs
I/FS50 with ARC
Magnetic Field Compatibility Option (MFC)
HINDS PRODUCT SOLUTIONS
MOKE Complete Solution Packages
FURTHER READING
Bennemann K.H., (Ed), Nonlinear Optics in Metals, Clarendon Press, Oxford, (1998).
Magneto-Optic Kerr Effect
Magnetism in a New Light
Contact us for additional information about using PEMs in a Magneto-Optic set-up.